The importance and application of blood oxygen saturation sensor for patients with respiratory diseases
2024-03-21 00:03:27
The Importance and Application of Blood Oxygen Saturation Sensor
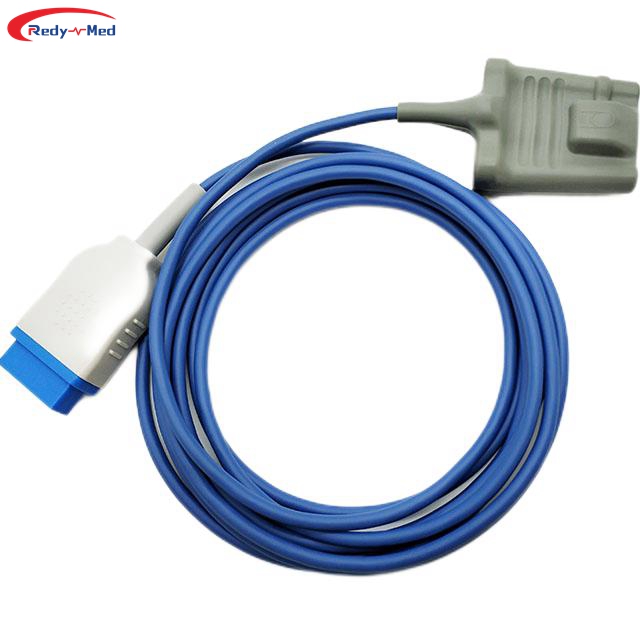

Respiratory diseases pose a significant threat to human health, affecting millions of people worldwide. Effectively managing these conditions requires accurate and timely monitoring of critical parameters such as blood oxygen saturation levels. The advancement of medical technology has revolutionized respiratory care, with the introduction of blood oxygen saturation sensors playing a pivotal role. This article explores the importance and wide-ranging applications of blood oxygen saturation sensors for patients with respiratory diseases.
1. Monitoring Oxygen Levels - Ensuring Optimal Patient Care
Blood oxygen saturation, commonly referred to as SpO2, indicates the percentage of oxygen-binding sites on hemoglobin that are occupied by oxygen molecules in the blood. For patients with respiratory diseases, accurate and real-time SpO2 monitoring is crucial to ensure sufficient oxygen supply to vital organs and tissues.
Blood oxygen saturation sensors, usually employed via pulse oximeters, provide a non-invasive and continuous method to monitor SpO2 levels. These sensors can be effortlessly attached to a patient's fingertip, earlobe, or forehead, instantly providing valuable data to healthcare professionals. This real-time monitoring enables healthcare providers to promptly detect any fluctuations or abnormalities in oxygen levels, allowing for immediate intervention and adjustment of treatment plans.
2. Diagnostic Aid - Early Detection and Proactive Management
Beyond real-time monitoring, blood oxygen saturation sensors also serve as a diagnostic aid for respiratory diseases. By continuously tracking SpO2 levels, healthcare professionals can identify patterns and trends that may indicate the presence of underlying conditions or the progression of respiratory diseases. This early detection allows for proactive management, preventing exacerbations and potentially reducing the severity of respiratory complications.
Moreover, blood oxygen saturation sensors can assist in differentiating between various respiratory disorders. For instance, obstructive sleep apnea, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary fibrosis have distinct SpO2 patterns during different sleep stages or physical activities. By analyzing these variations, clinicians can make accurate diagnoses and tailor treatment plans to individual patients.
3. Home Monitoring - Empowering Patients for Better Self-Management
Blood oxygen saturation sensors have become increasingly compact, affordable, and user-friendly, making them suitable for home monitoring purposes. Patients with respiratory diseases can now actively participate in managing their health by regularly tracking their SpO2 levels in the comfort of their own homes.
This home monitoring approach allows patients to identify triggers or potential exacerbating factors that contribute to fluctuating oxygen levels. By maintaining a log of SpO2 readings, individuals can proactively make lifestyle modifications, seek timely medical intervention, or adjust their medication regimen. Empowering patients with real-time data fosters self-management and enhances overall treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
The blood oxygen saturation sensor, together with pulse oximeters, plays a critical role in the comprehensive management of respiratory diseases. By enabling real-time monitoring, aiding in diagnosis, and empowering patients with home monitoring capabilities, these sensors have become indispensable tools for healthcare professionals and patients alike. The application of blood oxygen saturation sensors continues to advance respiratory care by ensuring optimal patient care, facilitating early detection, and enhancing self-management, leading to improved quality of life for individuals with respiratory diseases.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)