Application and principle introduction of blood oxygen saturation probe
2024-03-21 00:03:27
Overview and Functions
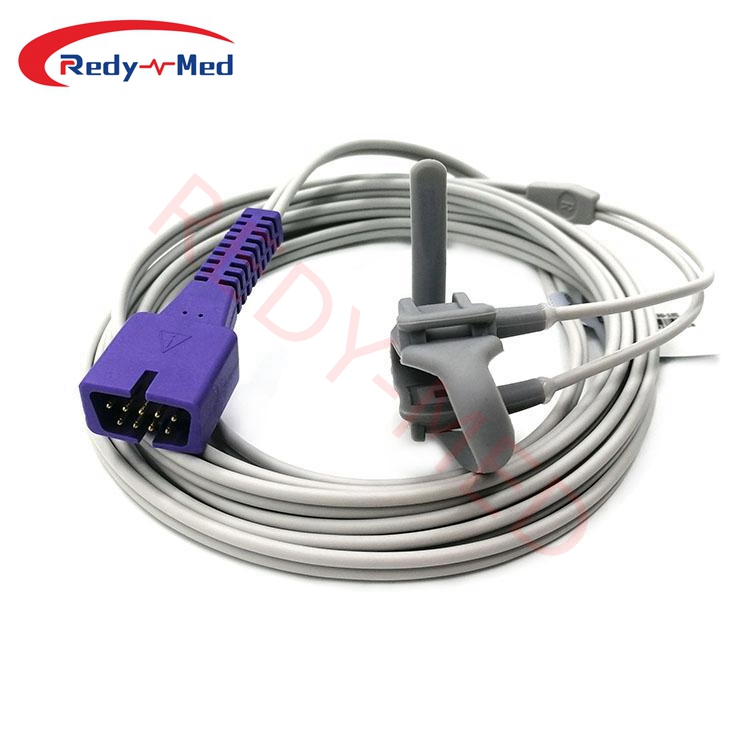

The blood oxygen saturation probe, also known as a pulse oximeter, is a medical device that measures the oxygen saturation level in a person's blood. It is widely used in various clinical settings such as hospitals, clinics, and home healthcare. The probe works by emitting and detecting light waves that pass through the skin and blood vessels.
One of the primary functions of the blood oxygen saturation probe is to monitor the oxygen saturation level of patients with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions. It provides vital information to healthcare professionals, allowing them to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make informed decisions regarding patient care. Additionally, the probe is used during surgeries and anesthesia to ensure the patient's safety and monitor their oxygen levels continuously.
Blood oxygen saturation is measured in terms of SpO2, which stands for peripheral capillary oxygen saturation. It is expressed as a percentage and indicates the amount of oxygen bound to hemoglobin in the blood. Normal blood oxygen saturation levels range from 95% to 100%, with values below 90% considered low and potentially indicative of hypoxemia.
Principle of Operation
The blood oxygen saturation probe operates based on the principle of spectrophotometry. It utilizes two light-emitting diodes (LEDs), typically red and infrared, which emit specific wavelengths of light. These light waves penetrate the skin and tissues and pass through the blood vessels.
Oxygenated hemoglobin and deoxygenated hemoglobin have different absorption characteristics for these two wavelengths of light. The probe's photodetector measures the amount of light absorbed and calculates the oxygen saturation level accordingly. This data is then displayed on the device's screen or transmitted to a monitor for continuous monitoring and analysis.
Furthermore, the pulse oximeter's probe also measures the patient's heart rate by analyzing the pulsatile nature of blood flow. It detects variations in light absorption caused by the pulsations and derives the heart rate from the collected data.
Advantages and Limitations
The blood oxygen saturation probe offers several advantages in clinical practice. It is non-invasive, convenient, and provides immediate results. Its compact and portable design allows for easy transportation and usage in various settings. Patients can wear the probe continuously, enabling continuous monitoring of oxygen levels during activities and sleep.
However, it is important to note that the blood oxygen saturation probe has certain limitations. Factors such as poor peripheral perfusion, motion artifacts, and certain medical conditions, such as anemia or carbon monoxide poisoning, may affect the accuracy of SpO2 measurements. In such cases, alternative methods or further diagnostic tests may be required to assess oxygenation adequately.
Conclusion
The blood oxygen saturation probe is a valuable tool in healthcare, providing valuable information about a patient's oxygenation status. Its non-invasive nature, ease of use, and real-time monitoring capabilities make it an essential device in various healthcare settings. However, clinicians must be aware of its limitations and consider other factors when interpreting the SpO2 measurements.
In summary, the blood oxygen saturation probe plays a vital role in assessing and monitoring a patient's oxygen levels accurately. Its principle of operation based on spectrophotometry allows for non-invasive and convenient measurement, aiding in prompt and informed decision-making for patient care.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)