The difference between electrocardiogram and ambulatory electrocardiogram
2024-03-21 00:04:21
Introduction
Electrocardiogram (ECG) and ambulatory electrocardiogram (AECG) are two widely used diagnostic techniques in cardiology. While both methods provide valuable information about the heart's electrical activity, they differ significantly in terms of procedure, duration, and applications. This article aims to explore the dissimilarities between ECG and AECG, highlighting their unique features and advantages.1. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
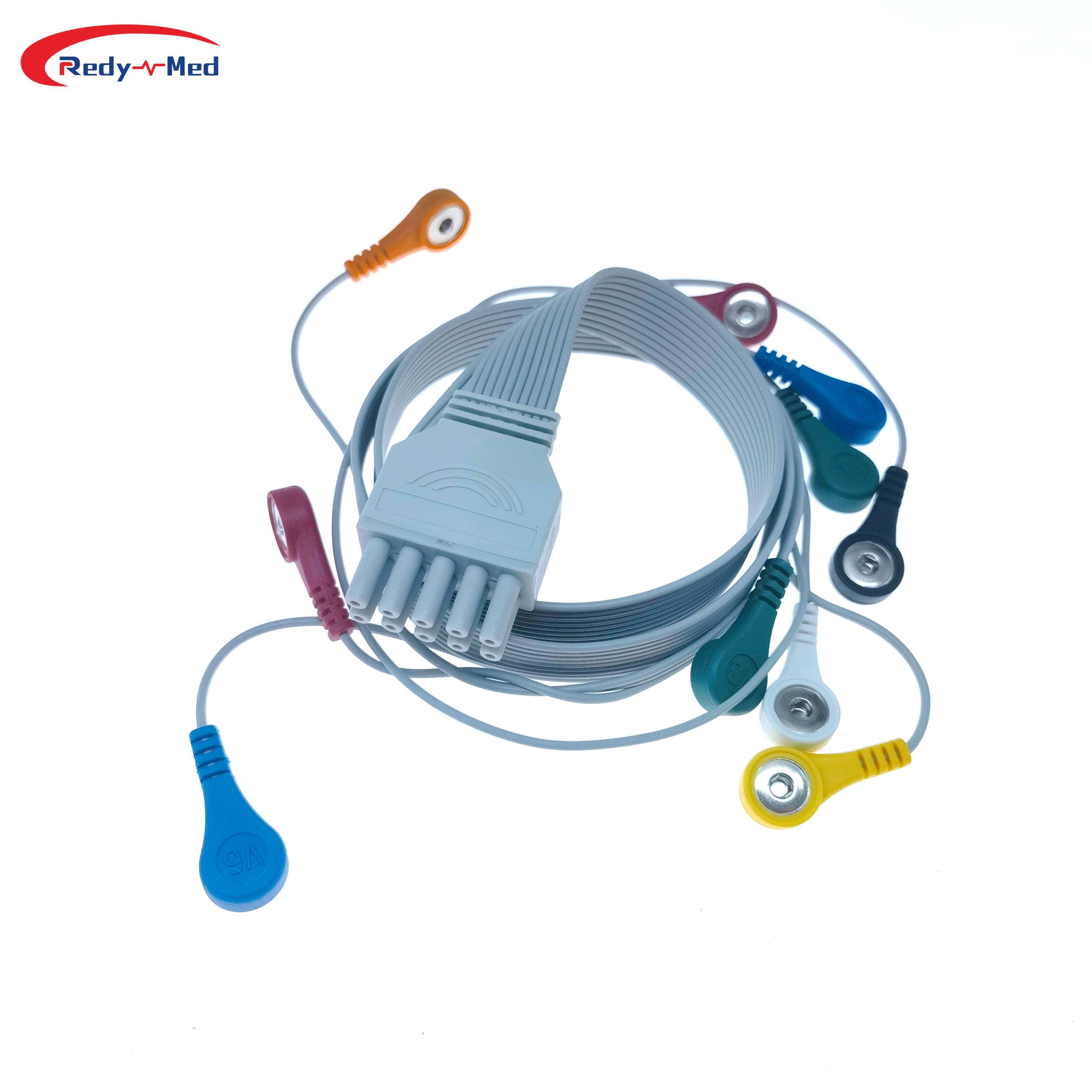

An ECG, often referred to as a standard ECG, is a non-invasive medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart. The procedure involves attaching electrodes to specific locations on the patient's chest, arms, and legs, which detect the electrical signals generated by the heart.
ECG results are presented as a graph, known as an electrocardiogram, which displays the heart's rhythm and helps diagnose various heart conditions. It is a quick and painless test that typically takes only a few minutes to complete.
Advantages of ECG:
- Quick and easy to perform, providing immediate results. - Useful in diagnosing acute heart conditions, such as myocardial infarction. - Cost-effective and widely available in healthcare settings.
2. Ambulatory Electrocardiogram (AECG)
An AECG, also known as a Holter monitor, is a portable device that continuously records the heart's electrical activity for an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours. It involves attaching electrodes to the patient's chest, similar to an ECG, and carrying a small recording device throughout their daily activities.
Unlike a standard ECG, an AECG provides a more comprehensive evaluation of the heart's electrical patterns over an extended period. This extended monitoring period allows for the detection of irregularities that may not be captured during a short ECG recording.
Advantages of AECG:
- Enables the detection of intermittent cardiac arrhythmias that may be missed in a standard ECG. - Provides a broader view of the heart's activity during daily life, capturing abnormalities that occur during physical exertion or sleep. - Helps evaluate the effectiveness of anti-arrhythmic medications or interventions.
3. Differences between ECG and AECG
Procedure: ECG is a one-time test performed in a healthcare setting, while AECG involves wearing a portable device for an extended period.
Duration: ECG usually takes a few minutes, while AECG records the heart's activity over 24 to 48 hours.
Applications: ECG is suitable for diagnosing acute conditions, while AECG is preferred for evaluating chronic or intermittent abnormalities.
Availability: ECG is available in most healthcare facilities, while AECG requires specialized devices and data analysis.
Summary
Both ECG and AECG play crucial roles in diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions. While an ECG provides a quick snapshot of the heart's electrical activity, an AECG offers a more comprehensive evaluation over an extended period. AECG is particularly useful in detecting intermittent arrhythmias and assessing the effectiveness of treatments. Understanding the differences between these two techniques allows healthcare professionals to choose the most appropriate diagnostic method based on the patient's needs.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)