mainstream vs sidestream etco2
2024-03-21 00:04:27
Understanding the Differences and Advantages
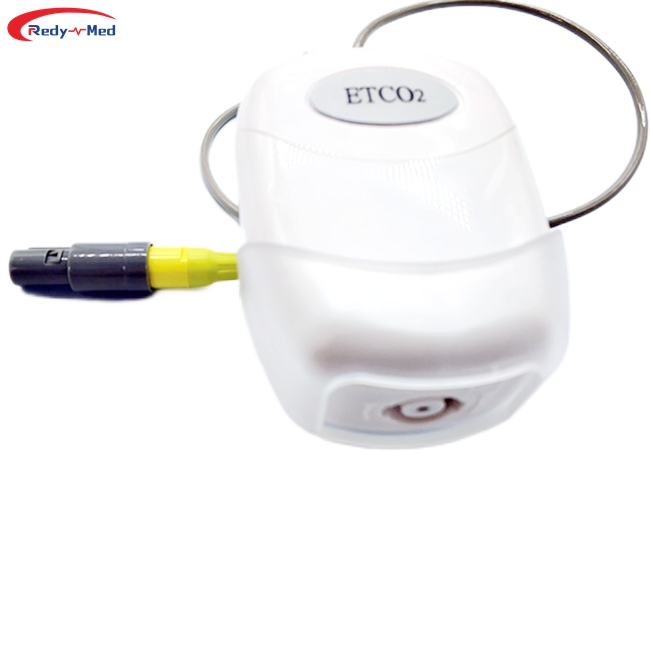

End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) monitoring is an essential tool used in various medical settings, particularly during anesthesia and critical care procedures. Mainstream and sidestream ETCO2 are two different approaches to measure and analyze carbon dioxide levels in exhaled breath. In this article, we will explore the differences between mainstream and sidestream ETCO2, highlighting their advantages and applications.
Mainstream ETCO2 Monitoring
Mainstream ETCO2 monitoring involves the use of a sensor that is placed directly in the breathing circuit of the patient. This sensor measures the carbon dioxide levels in real-time throughout the respiratory cycle. The mainstream method offers several advantages:
- Accurate and continuous monitoring: As the sensor is placed directly in the breathing circuit, it provides real-time readings of ETCO2 levels, ensuring accurate monitoring throughout the entire respiratory cycle.
- Fast response time: Mainstream ETCO2 monitoring has a quick response time, allowing healthcare professionals to detect any sudden changes in carbon dioxide levels promptly.
- Minimal delay in measurement: Since the sensor is closer to the patient's airway, there is minimal delay in the measurement of ETCO2 levels, providing immediate feedback on respiratory status.
Sidestream ETCO2 Monitoring
Sidestream ETCO2 monitoring, on the other hand, involves the use of a sample line connected to the patient's airway. It diverts a small portion of the exhaled breath to an analyzer, where the carbon dioxide levels are measured. Sidestream ETCO2 monitoring has its own set of advantages:
- Flexible placement: The sample line used in sidestream ETCO2 monitoring allows for flexibility in sensor placement, making it suitable for various patient settings.
- Reduced infection risk: As the sensor is not directly placed in the breathing circuit, sidestream ETCO2 monitoring has a lower risk of contamination or infection.
- Compatibility with non-intubated patients: Sidestream ETCO2 monitoring can be used in non-intubated patients by utilizing a nasal cannula or a mask, expanding its applicability.
Conclusion
In summary, both mainstream and sidestream ETCO2 monitoring have their unique advantages and applications. Mainstream ETCO2 provides accurate and continuous monitoring with a fast response time, making it ideal for critical and anesthesia care. Sidestream ETCO2, on the other hand, offers flexibility in sensor placement and reduced infection risks, making it suitable for non-intubated patients and certain clinical settings.
The choice between mainstream and sidestream ETCO2 monitoring depends on the specific requirements of the procedure and patient condition. Understanding the differences and advantages of each approach enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions for optimal patient care.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)